Athens vs sparta venn diagram – Athens vs Sparta: A Tale of Two City-States sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
This in-depth exploration delves into the historical significance, political systems, military prowess, cultural nuances, economic structures, and artistic achievements of these two iconic city-states, providing a comprehensive understanding of their profound impact on Western civilization.
Historical Background
Athens and Sparta were two of the most powerful and influential city-states in ancient Greece. They played a major role in shaping the course of Greek history and left a lasting legacy on Western civilization.
Origins and Development
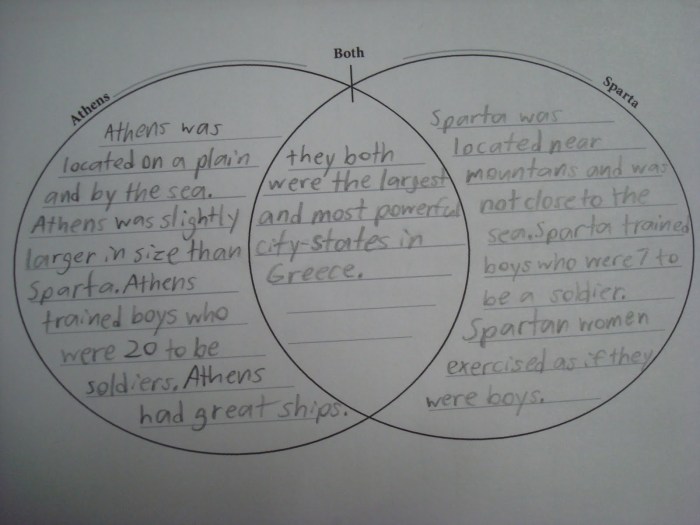
Athens was founded in the 15th century BC, while Sparta was founded in the 10th century BC. Both cities grew rapidly and became major centers of trade and culture. Athens was known for its democratic government and its flourishing arts and sciences, while Sparta was known for its powerful military and its strict social hierarchy.
Key Events in the History of Athens and Sparta
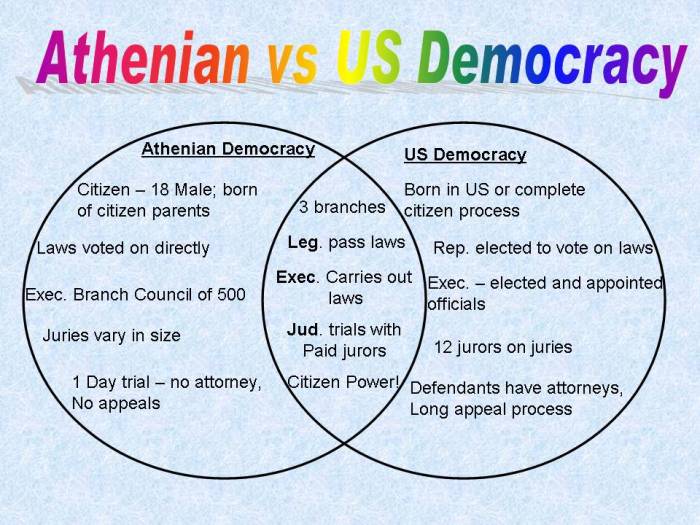
- Athenian Democracy: Athens established a democratic government in the 5th century BC, which allowed all male citizens to participate in the political process.
- Spartan Military: Sparta developed a powerful military based on the phalanx formation, which made them one of the most formidable armies in the ancient world.
- Peloponnesian War: Athens and Sparta fought a devastating war from 431 to 404 BC, which ended with the defeat of Athens and the establishment of Spartan hegemony over Greece.
Political Systems
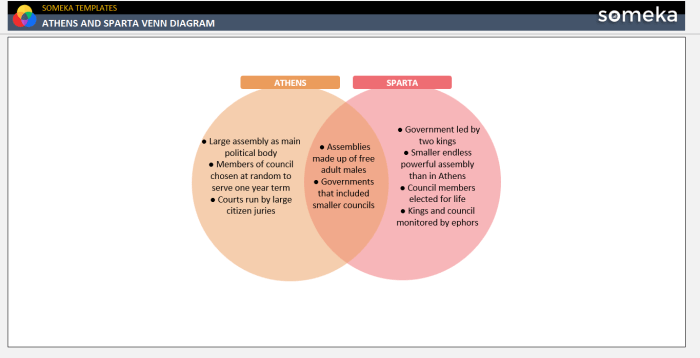
Athens and Sparta were two powerful city-states in ancient Greece, but their political systems were vastly different. Athens was a democracy, while Sparta was an oligarchy. In Athens, all male citizens had a say in the government, while in Sparta, only a small group of wealthy landowners held political power.
Role of Citizens and Non-Citizens
In Athens, all male citizens over the age of 18 were eligible to participate in the Assembly, which was the main governing body of the city-state. The Assembly met regularly to discuss and vote on laws, elect officials, and declare war.
In Sparta, only a small group of wealthy landowners, known as the Spartiates, had full political rights. The Spartiates controlled the Assembly and all other government offices. Non-citizens, known as helots, had no political rights and were forced to work the land for the Spartiates.
Distribution of Political Power
In Athens, political power was distributed more evenly among the citizens than in Sparta. The Assembly was the supreme governing body, and all citizens had an equal say in its decisions. In Sparta, political power was concentrated in the hands of the Spartiates, who controlled the Assembly and all other government offices.
Military Strength
Athens and Sparta possessed distinct military strengths and weaknesses. This section analyzes their military capabilities, training methods, and strategic approaches.
Training and Organization
Spartan soldiers underwent rigorous training from childhood, emphasizing discipline, physical fitness, and obedience. Their army was organized into phalanxes, tight formations of heavily armed hoplites wielding long spears and large shields.
In contrast, Athenian soldiers received less formal training, but they were more adaptable and versatile. Their army included hoplites, cavalry, and a powerful navy.
Military Strategies and Tactics
Sparta relied heavily on its phalanx formation, emphasizing close-order combat and frontal assaults. Their tactics aimed to break enemy lines through sheer force and discipline.
Athens employed a more flexible approach, using its navy to control sea lanes and support land operations. They also utilized cavalry for reconnaissance and harassment.
Cultural Differences
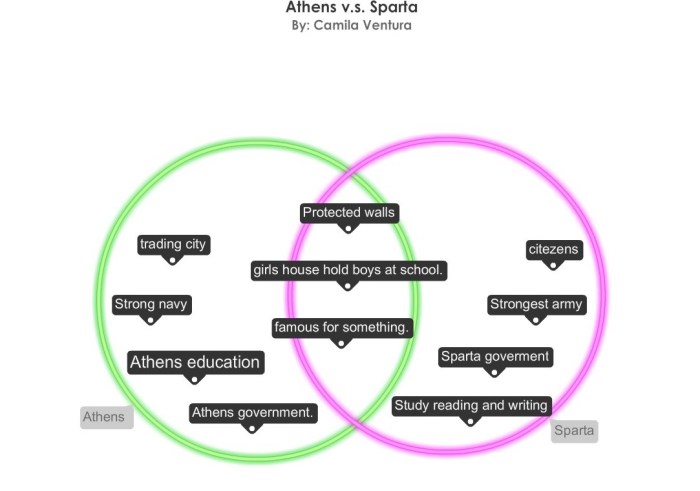
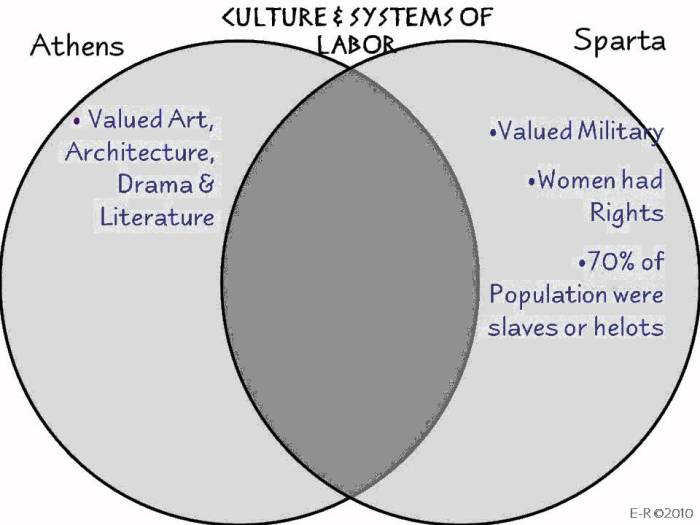
Athens and Sparta exhibited stark cultural differences that permeated their daily lives and interactions. Athenian culture emphasized intellectualism, philosophy, and artistic expression, while Spartan society prioritized military prowess and discipline.
The ancient rivalry between Athens and Sparta can be analyzed using a Venn diagram, highlighting their similarities and differences. Intriguingly, there’s also a way to explore your potential Viking ancestry with the do I have Viking blood quiz . Returning to our Athens vs.
Sparta comparison, this diagram can provide valuable insights into the distinct characteristics of these two prominent Greek city-states.
Athenian Culture, Athens vs sparta venn diagram
Athenians valued intellectual pursuits, with a flourishing of philosophers, poets, and artists. They placed great importance on education and critical thinking, believing that an informed citizenry was essential for a strong and just society. Athenian culture celebrated individual expression and creativity, fostering a vibrant intellectual and artistic scene.
Spartan Culture
In contrast, Spartan culture revolved around military preparedness and discipline. Spartans underwent rigorous training from childhood, instilling in them a sense of obedience, self-sacrifice, and loyalty to the state. They emphasized physical strength, endurance, and a strict adherence to military regulations.
Individualism was discouraged in favor of collective interests, with the well-being of the community taking precedence over personal desires.These cultural differences had a profound impact on the daily lives of Athenians and Spartans. Athenians enjoyed a more relaxed and cosmopolitan lifestyle, engaging in philosophical debates, attending theatrical performances, and participating in public assemblies.
Spartans, on the other hand, lived under a rigid regime of training and discipline, with little time for leisure or intellectual pursuits.The cultural divide between Athens and Sparta extended to their beliefs and customs. Athenians believed in the power of reason and the importance of individual rights, while Spartans adhered to a more traditional and authoritarian worldview that emphasized the authority of the state.
These differences shaped their political systems, military strategies, and social interactions, ultimately contributing to the rivalry and conflict between the two city-states.
Economic Systems

Athens and Sparta possessed contrasting economic systems that significantly influenced their societies and political structures.
Athens thrived as a maritime and commercial hub. Its economy relied heavily on trade, with the city serving as a major port and marketplace. Athenian merchants traded a wide range of goods, including olive oil, wine, pottery, and metalwork. The city also benefited from its silver mines, which provided a substantial source of wealth.
Sparta, on the other hand, adopted an agrarian economy. Its focus was on agriculture, with land ownership concentrated among a small elite class. The Spartan government strictly regulated economic activities, aiming to maintain social stability and prevent the accumulation of wealth by individuals.
Major Industries and Sources of Wealth
- Athens:Trade, shipping, olive oil production, pottery, metalwork, silver mining
- Sparta:Agriculture, land ownership, iron production
Impact on Social and Political Life
The economic systems of Athens and Sparta shaped the social and political dynamics of each city-state.
In Athens, the commercial economy led to a more open and diverse society. Wealth was not solely concentrated among the elite, and citizens had opportunities for economic advancement through trade and commerce. This fostered a sense of individualism and democratic values.
In Sparta, the agrarian economy reinforced the rigid social hierarchy. The elite landowners held political power and controlled the distribution of wealth. This system stifled economic mobility and contributed to the militaristic culture of Spartan society.
Artistic and Intellectual Achievements
Athens and Sparta made significant contributions to the artistic and intellectual landscape of ancient Greece, leaving a lasting legacy that has influenced Western civilization.
Philosophy
Athens was renowned as the birthplace of philosophy. Athenian philosophers such as Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle developed influential ideas about ethics, politics, and metaphysics that continue to be studied and debated today.
Literature
Both Athens and Sparta produced notable works of literature. Athens was home to renowned playwrights like Sophocles, Euripides, and Aristophanes, whose tragedies and comedies explored themes of human nature and society.
Art
Athenian art was characterized by its emphasis on beauty, realism, and humanism. Sculptures like the “Venus de Milo” and the “Discobolus” exemplified the idealization of the human form.
Architecture
Athens and Sparta had distinct architectural styles. Athens is known for its monumental temples, such as the Parthenon, which represented the pinnacle of classical Greek architecture. Sparta, on the other hand, favored functional and austere buildings, prioritizing military efficiency.
Answers to Common Questions: Athens Vs Sparta Venn Diagram
What were the key differences between Athens and Sparta?
Athens was a democratic city-state known for its cultural and intellectual achievements, while Sparta was a militaristic society with a rigid social hierarchy.
Which city-state was more powerful militarily?
Sparta had a formidable army and was considered the dominant military power in Greece.
What were the major economic activities in Athens and Sparta?
Athens was a major trading center, while Sparta relied heavily on agriculture.