Phase change worksheet answer key unveils the intricacies of phase changes, guiding learners through the fascinating processes that shape our world. From the melting of ice to the condensation of steam, this key unlocks a deeper understanding of matter’s transformations.
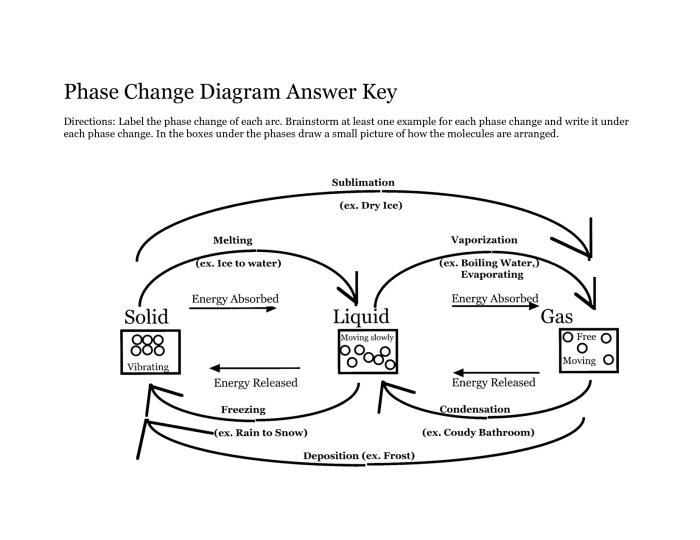
Delving into the realm of phase changes, we explore the different types, including melting, freezing, vaporization, and condensation, and unravel the energy changes associated with each. We investigate the factors influencing the rate and extent of phase changes, such as temperature, pressure, and surface area, revealing how these factors impact the equilibrium between phases.
1. Define Phase Change
Phase change refers to the transformation of a substance from one state to another, such as from solid to liquid, liquid to gas, or vice versa. It involves changes in the molecular structure and intermolecular forces within the substance.
2. Types of Phase Changes
Melting
Melting is the transition from a solid to a liquid state. It occurs when the temperature of a solid is raised, causing the molecules to gain kinetic energy and break free from their fixed positions in the crystal lattice.
Freezing
Freezing is the reverse of melting, where a liquid is transformed into a solid. It occurs when the temperature of a liquid is lowered, causing the molecules to lose kinetic energy and arrange themselves into a more ordered, crystalline structure.
Vaporization, Phase change worksheet answer key
Vaporization refers to the transformation of a liquid or solid into a gas. It occurs when the temperature of a substance is raised to its boiling point, causing the molecules to gain enough energy to overcome the intermolecular forces and escape into the gaseous phase.
Condensation
Condensation is the opposite of vaporization, where a gas is transformed into a liquid or solid. It occurs when the temperature of a gas is lowered, causing the molecules to lose kinetic energy and condense into a more condensed phase.
3. Factors Affecting Phase Changes
Several factors influence the rate and extent of phase changes, including:
- Temperature:Temperature plays a crucial role in phase changes, as it determines the kinetic energy of molecules and their ability to overcome intermolecular forces.
- Pressure:Pressure can affect the melting and boiling points of substances. For example, increasing pressure raises the melting point of water but lowers its boiling point.
- Surface Area:For substances with a large surface area, phase changes can occur more rapidly due to increased exposure to the surrounding environment.
4. Applications of Phase Changes
Phase changes have numerous practical applications in various fields:
- Heating and Cooling:Phase changes are utilized in heating and cooling systems, such as air conditioners and refrigerators, to transfer heat from one place to another.
- Manufacturing:Phase changes are employed in manufacturing processes, such as casting, molding, and welding, to shape and form materials.
- Food Preservation:Phase changes are used in food preservation techniques, such as freezing and canning, to extend the shelf life of perishable items.
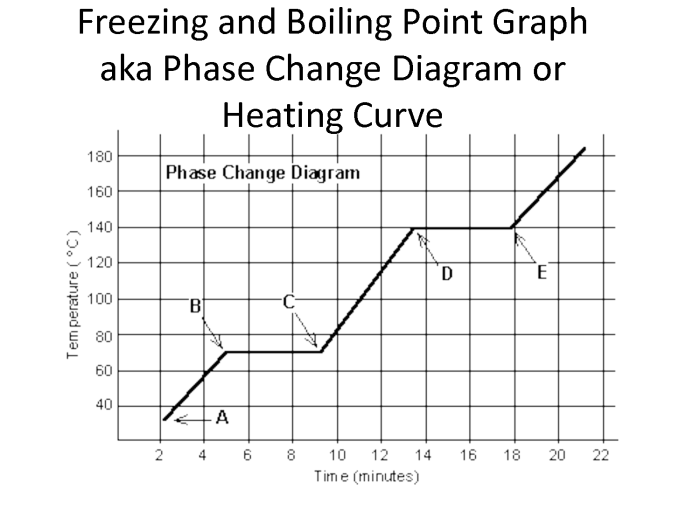
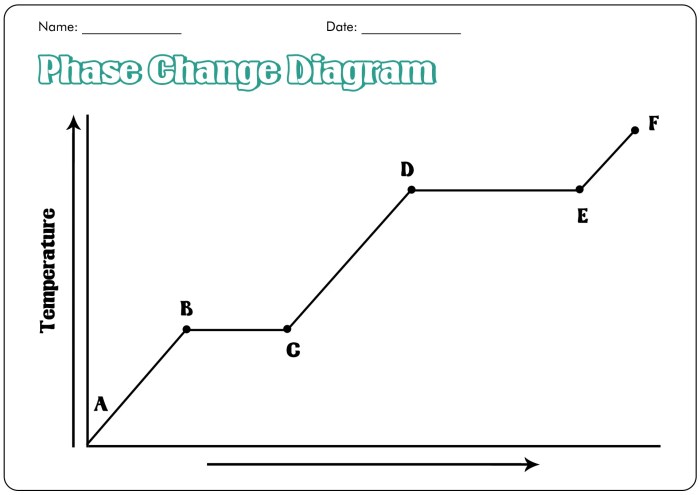
5. Phase Change Diagrams
Phase change diagrams are graphical representations that depict the phase behavior of substances under varying temperature and pressure conditions. They provide information about the melting point, boiling point, and other phase transition points of a substance.
6. Latent Heat: Phase Change Worksheet Answer Key
Latent heat refers to the amount of energy absorbed or released by a substance during a phase change without a change in temperature. There are two types of latent heat:
- Latent Heat of Fusion:The energy required to melt a solid into a liquid at its melting point.
- Latent Heat of Vaporization:The energy required to vaporize a liquid into a gas at its boiling point.
7. Energy Conservation in Phase Changes
During phase changes, energy is conserved. The energy absorbed or released during a phase change is equal to the latent heat of the substance.
Quick FAQs
What is a phase change?
A phase change is a physical process in which a substance undergoes a change in its state of matter, such as from solid to liquid or liquid to gas.
What are the different types of phase changes?
The main types of phase changes are melting, freezing, vaporization, and condensation.
What factors affect the rate of a phase change?
Factors affecting the rate of a phase change include temperature, pressure, and surface area.