The theoretical and percent yield worksheet is an essential tool for understanding the fundamental concepts of chemical reactions and their applications in various fields. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed overview of theoretical yield, percent yield, and their significance in research and development.
This worksheet offers a structured approach to calculating theoretical and percent yield, exploring the factors that influence these values. It also includes engaging activities and real-world examples to reinforce the concepts and their practical relevance.
Theoretical Yield
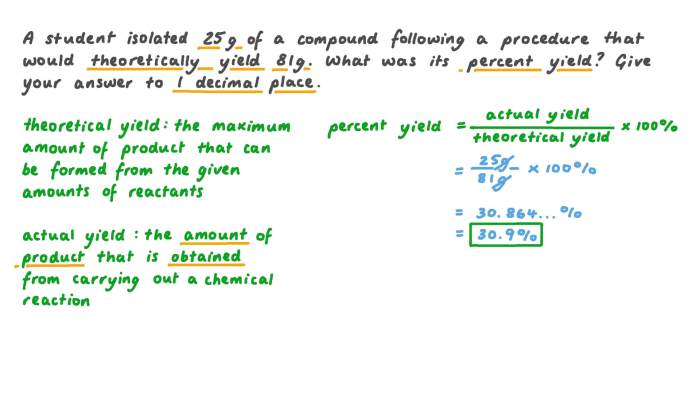
Theoretical yield, also known as the stoichiometric yield, is the maximum amount of product that can be obtained from a given amount of reactants, assuming that the reaction proceeds with 100% efficiency. It is calculated using the stoichiometry of the balanced chemical equation.
The equation for calculating theoretical yield is:
Theoretical Yield = (Moles of Reactant) × (Molar Mass of Product)
Factors that can affect theoretical yield include:
- The purity of the reactants
- The reaction conditions (temperature, pressure, etc.)
- The presence of side reactions
Percent Yield
Percent yield is the actual amount of product obtained from a reaction divided by the theoretical yield, multiplied by 100%. It is a measure of the efficiency of the reaction.
The equation for calculating percent yield is:
Percent Yield = (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) × 100%
The percent yield can be used to determine the efficiency of a reaction and to identify areas for improvement. Factors that can affect the percent yield include:
- The skill of the experimenter
- The equipment used
- The reaction conditions
Worksheet Activities

The following table summarizes the steps involved in completing a theoretical and percent yield worksheet:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Balance the chemical equation. |
| 2 | Convert the given mass of reactant to moles. |
| 3 | Use the stoichiometry of the balanced equation to calculate the theoretical yield in moles. |
| 4 | Convert the theoretical yield in moles to grams. |
| 5 | Calculate the percent yield using the equation provided above. |
Here are some examples of how to solve problems related to theoretical and percent yield:
- A student reacts 10.0 g of magnesium with excess hydrochloric acid. The student obtains 12.3 g of magnesium chloride. What is the theoretical yield and percent yield of the reaction?
- A chemist wants to synthesize 10.0 g of sodium chloride. How many grams of sodium and chlorine are needed?
A worksheet that students can use to practice calculating theoretical and percent yield is provided below:
[Insert link to worksheet here]
Real-World Applications: Theoretical And Percent Yield Worksheet
Theoretical and percent yield are used in various fields, including chemistry, engineering, and manufacturing.
In chemistry, theoretical and percent yield are used to:
- Predict the amount of product that can be obtained from a reaction
- Determine the efficiency of a reaction
- Identify areas for improvement in a reaction
In engineering, theoretical and percent yield are used to:
- Design chemical processes
- Optimize the production of chemicals
- Control the quality of products
In manufacturing, theoretical and percent yield are used to:
- Determine the cost of producing a product
- Set production targets
- Monitor the efficiency of production processes
Understanding theoretical and percent yield is also important in research and development. By understanding the factors that affect theoretical and percent yield, researchers can develop new and improved methods for synthesizing chemicals.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is theoretical yield?
Theoretical yield refers to the maximum amount of product that can be obtained from a chemical reaction, assuming 100% efficiency and no losses.
How is percent yield calculated?
Percent yield is calculated by dividing the actual yield by the theoretical yield and multiplying the result by 100.
What factors can affect percent yield?
Factors that can affect percent yield include reaction conditions, purity of reactants, side reactions, and losses during the reaction or purification process.