For a continuous and oriented fiber reinforced composite – Continuous and oriented fiber reinforced composites have emerged as advanced materials that offer exceptional properties, making them highly sought after in various industries. This article delves into the composition, manufacturing process, mechanical characteristics, applications, and advantages and disadvantages of these remarkable composites.
Their unique combination of strength, stiffness, and durability stems from the continuous and aligned fibers embedded within a matrix material, resulting in composites that surpass traditional materials in many aspects.
Continuous and Oriented Fiber Reinforced Composites: For A Continuous And Oriented Fiber Reinforced Composite
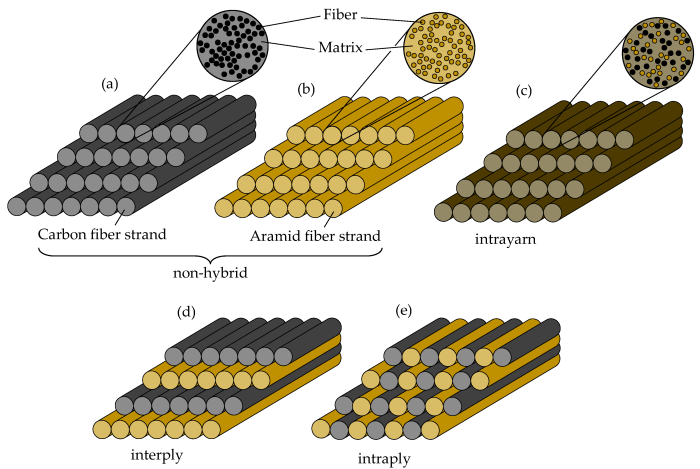
Continuous and oriented fiber reinforced composites are a type of advanced composite material that consists of continuous fibers embedded in a matrix material. The fibers are typically made of high-strength materials such as carbon, glass, or aramid, while the matrix material can be a polymer, metal, or ceramic.
These composites are characterized by their high strength, stiffness, and durability, making them ideal for use in a wide range of applications.
Materials, For a continuous and oriented fiber reinforced composite
The properties and characteristics of continuous and oriented fiber reinforced composites are determined by the materials used to make them. The fibers provide the composite with its strength and stiffness, while the matrix material provides support and protection for the fibers.The
most common type of fiber used in continuous and oriented fiber reinforced composites is carbon fiber. Carbon fiber is a strong, stiff, and lightweight material that is resistant to corrosion and heat. Other types of fibers that can be used include glass fiber, aramid fiber, and boron fiber.The
matrix material in continuous and oriented fiber reinforced composites can be a polymer, metal, or ceramic. The most common type of polymer matrix is epoxy resin. Epoxy resin is a strong, tough, and lightweight material that is resistant to chemicals and heat.
Other types of polymer matrices that can be used include polyester resin, vinyl ester resin, and phenolic resin.Metal matrix composites are typically made with aluminum or titanium. Metal matrix composites offer high strength and stiffness, as well as good thermal conductivity.
Ceramic matrix composites are made with ceramic materials such as alumina or silicon carbide. Ceramic matrix composites offer high strength, stiffness, and hardness, as well as good thermal stability.
Manufacturing Process
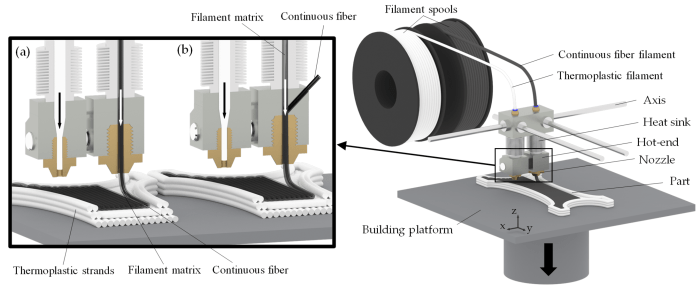
The manufacturing process for continuous and oriented fiber reinforced composites involves several steps. The first step is to prepare the fibers. The fibers are typically coated with a sizing agent to improve their adhesion to the matrix material. The fibers are then aligned in the desired orientation and placed in a mold.The
next step is to add the matrix material. The matrix material can be applied in a variety of ways, including hand lay-up, spray-up, and vacuum infusion. Once the matrix material has been applied, the composite is cured. Curing can be done at room temperature or at elevated temperatures.The
final step in the manufacturing process is to finish the composite. This may involve trimming the edges of the composite, sanding the surface, or painting the composite.
Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties of continuous and oriented fiber reinforced composites are superior to those of most other materials. These composites have high strength, stiffness, and durability. They are also resistant to corrosion and fatigue.The tensile strength of continuous and oriented fiber reinforced composites is typically in the range of 100-1,000 MPa.
The flexural strength of these composites is typically in the range of 200-1,500 MPa. The impact resistance of these composites is typically in the range of 10-100 J/m.The mechanical properties of continuous and oriented fiber reinforced composites can be tailored to meet the specific requirements of an application.
By varying the type of fiber, the orientation of the fibers, and the matrix material, it is possible to create composites with a wide range of properties.
Popular Questions
What are the key advantages of continuous and oriented fiber reinforced composites?
These composites offer high strength-to-weight ratios, excellent stiffness, enhanced durability, and corrosion resistance.
How are continuous and oriented fiber reinforced composites manufactured?
The manufacturing process involves preparing the fibers, aligning them in the desired orientation, and impregnating them with a matrix material, followed by curing.
In which industries are continuous and oriented fiber reinforced composites commonly used?
These composites find applications in aerospace, automotive, construction, and sports equipment due to their superior mechanical properties.