Literary tradition definition ap human geography – Literary Tradition Definition: A Comprehensive Overview for AP Human Geography delves into the fascinating world of literary traditions, providing an in-depth exploration of their definition, types, historical development, societal influence, and relevance to the study of human geography. Through a comprehensive examination of these literary traditions, we embark on a journey that unravels the intricate tapestry of human culture, beliefs, and experiences.
Literary traditions serve as a mirror to societal values, beliefs, and aspirations, shaping the cultural landscape and fostering a sense of collective identity. They offer a unique lens through which we can explore the human condition, gain insights into diverse perspectives, and trace the evolution of human thought and expression.
Definition of Literary Tradition
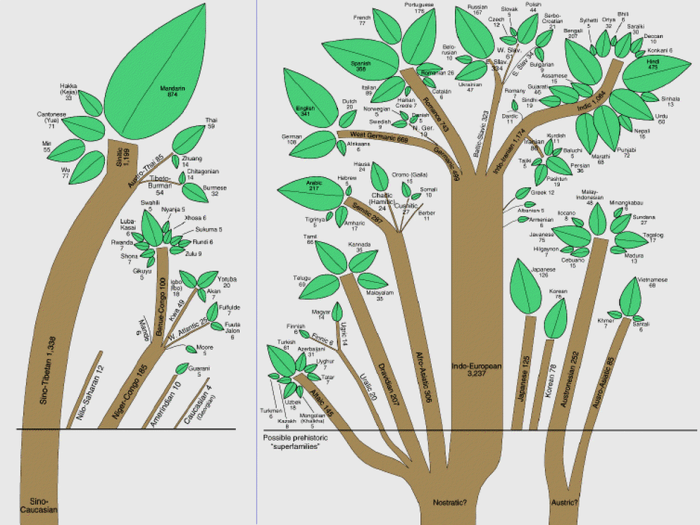
A literary tradition refers to a set of shared cultural values, beliefs, and literary practices that shape the production, interpretation, and reception of literature within a particular society or group.
Key elements that characterize a literary tradition include:
- Shared themes and motifs
- Common literary genres and forms
- Specific literary devices and techniques
- A sense of continuity and connection between literary works
Cultural values and beliefs play a significant role in shaping literary traditions. They influence the themes, characters, and narrative structures that are considered appropriate or desirable within a particular society.
Types of Literary Traditions: Literary Tradition Definition Ap Human Geography
There are various types of literary traditions, each with its unique characteristics:
- Oral traditions:Literature passed down through spoken word, such as folktales, myths, and legends.
- Written traditions:Literature that is recorded in written form, such as novels, plays, and poetry.
- Indigenous traditions:Literature created by indigenous communities, reflecting their cultural heritage and worldview.
- National traditions:Literature that reflects the shared history, values, and experiences of a nation.
- International traditions:Literature that transcends national boundaries and appeals to a global audience.
Each type of literary tradition has its own distinct themes, genres, and literary devices. For example, oral traditions often feature repetition, rhythm, and formulaic language, while written traditions may employ complex narrative structures and sophisticated literary techniques.
Historical Development of Literary Traditions

Literary traditions have evolved over time, influenced by social, political, and cultural changes.
- Ancient traditions:The earliest literary traditions emerged in ancient civilizations, such as Mesopotamia, Egypt, and Greece.
- Medieval traditions:During the Middle Ages, literary traditions were shaped by religious beliefs and feudalism.
- Renaissance and Enlightenment traditions:The Renaissance and Enlightenment periods saw a revival of classical learning and a focus on humanism.
- Romantic and Realist traditions:The Romantic era emphasized emotion and imagination, while Realism sought to depict everyday life accurately.
- Modern and Contemporary traditions:Modern and contemporary literary traditions are characterized by experimentation, diversity, and a global perspective.
Literary traditions have adapted and changed to reflect the changing needs and values of society.
The Influence of Literary Traditions on Society
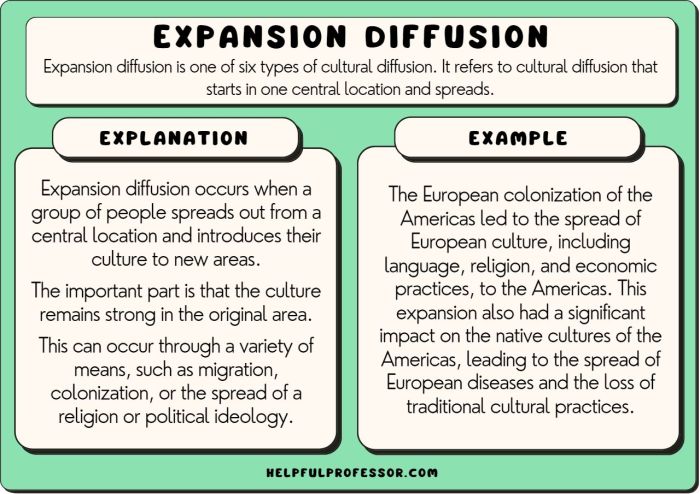
Literary traditions shape and reflect societal values and beliefs.
- Cultural identity:Literature can help to define and reinforce a sense of cultural identity by celebrating shared experiences and values.
- Social cohesion:Literature can foster social cohesion by providing a common ground for people to connect and engage with each other.
- Social movements:Literary works have played a significant role in inspiring and shaping social movements, such as the civil rights movement and the women’s rights movement.
- Political ideologies:Literature can reflect and critique political ideologies, providing insights into the power structures and values of a society.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the significance of literary traditions in the study of human geography?
Literary traditions provide valuable insights into cultural landscapes, social interactions, and environmental issues, offering geographers a unique perspective on human-environment relationships.
How do literary traditions reflect societal values and beliefs?
Literary traditions embody the shared cultural values, beliefs, and aspirations of a society, shaping the themes, characters, and narratives that resonate with its members.
What are the key elements that characterize a literary tradition?
Literary traditions are characterized by shared cultural values, beliefs, themes, genres, literary devices, and a sense of continuity over time.