Which molecule or compound below contains a polar covalent bond – Polar covalent bonds are a fundamental concept in chemistry, and they play a crucial role in determining the properties and behavior of molecules. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of polar covalent bonds, providing a clear understanding of their formation, characteristics, and significance.
Polar covalent bonds arise when atoms with different electronegativities share electrons, resulting in an unequal distribution of charge within the bond. This polarity has profound implications for molecular structure, reactivity, and interactions, making it an essential aspect of chemical bonding.
Definition of Polar Covalent Bond: Which Molecule Or Compound Below Contains A Polar Covalent Bond
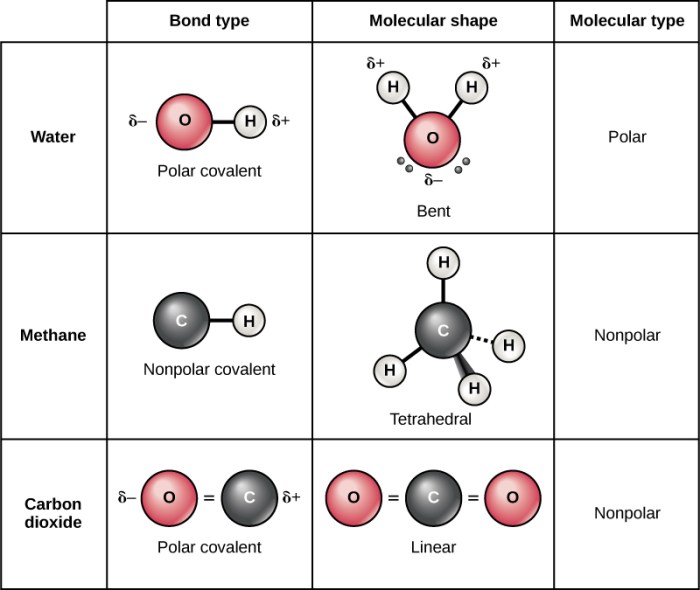
A polar covalent bond is a type of chemical bond in which the electrons are not shared equally between the two atoms involved. This results in a separation of charge, with one atom having a partial positive charge and the other having a partial negative charge.
The polarity of a covalent bond is determined by the difference in electronegativity between the two atoms.
Factors Influencing Polarity
Electronegativity Difference
The electronegativity of an atom is a measure of its ability to attract electrons. The greater the difference in electronegativity between two atoms, the more polar the covalent bond between them will be.
Molecular Geometry
The geometry of a molecule can also affect the polarity of its covalent bonds. Molecules with a symmetrical geometry, such as carbon dioxide, have nonpolar covalent bonds. Molecules with an asymmetrical geometry, such as water, have polar covalent bonds.
Identification of Polar Covalent Bonds
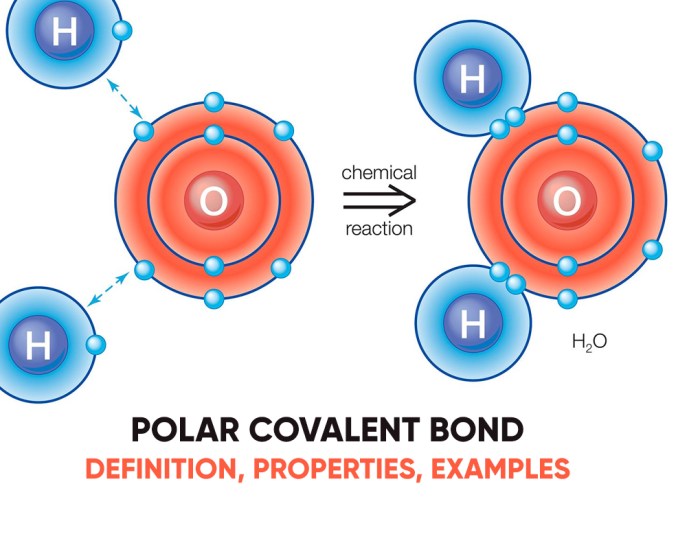
Table of Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
| Molecule | Electronegativity Difference | Bond Polarity |
|---|---|---|
| H2 | 0 | Nonpolar |
| HCl | 1.9 | Polar |
| NH3 | 0.9 | Polar |
| CO2 | 0 | Nonpolar |
Flowchart to Identify Polar Covalent Bonds
- Determine the electronegativity of each atom involved in the bond.
- Calculate the difference in electronegativity between the two atoms.
- If the difference in electronegativity is greater than 0.5, the bond is polar covalent.
- If the difference in electronegativity is less than or equal to 0.5, the bond is nonpolar covalent.
Consequences of Polarity
Impact of Polarity on Molecular Properties
The polarity of a molecule can affect its physical and chemical properties. Polar molecules are more likely to dissolve in water than nonpolar molecules. Polar molecules also have higher boiling points than nonpolar molecules.
Relationship between Polarity and Solubility, Which molecule or compound below contains a polar covalent bond
The polarity of a molecule can affect its solubility in different solvents. Polar molecules are more soluble in polar solvents, while nonpolar molecules are more soluble in nonpolar solvents.
Influence of Polarity on Chemical Reactions
The polarity of a molecule can also affect its reactivity. Polar molecules are more likely to react with other polar molecules, while nonpolar molecules are more likely to react with other nonpolar molecules.
Applications of Polarity
Practical Applications of Polar Covalent Bonds
- Polar covalent bonds are used in a variety of applications, including:
- The design of new drugs
- The separation of molecules using chromatography
- The development of new materials
FAQ Overview
What is the difference between a polar covalent bond and a nonpolar covalent bond?
In a polar covalent bond, the electrons are not shared equally between the atoms, resulting in a partial positive charge on one atom and a partial negative charge on the other. In a nonpolar covalent bond, the electrons are shared equally, resulting in no net charge separation.
What factors influence the polarity of a covalent bond?
The polarity of a covalent bond is primarily influenced by the electronegativity difference between the atoms involved. Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons. The greater the electronegativity difference, the more polar the bond.
How does polarity affect the properties of molecules?
Polarity influences various molecular properties, such as solubility, boiling point, and reactivity. Polar molecules tend to be more soluble in polar solvents and have higher boiling points than nonpolar molecules. Polarity also affects the reactivity of molecules, as polar molecules can participate in dipole-dipole interactions and hydrogen bonding.