Solutes and solvents quick check: Embark on an enlightening journey into the fascinating world of solutions, where we unravel the intricate relationship between solutes and solvents, exploring their types, factors affecting solubility, preparation methods, and myriad applications.
Delving into the depths of this captivating topic, we will uncover the fundamental concepts of solutes and solvents, unraveling their distinct characteristics and interactions. Together, we will embark on a quest to decipher the factors that govern solubility, empowering us to manipulate solutions with precision.
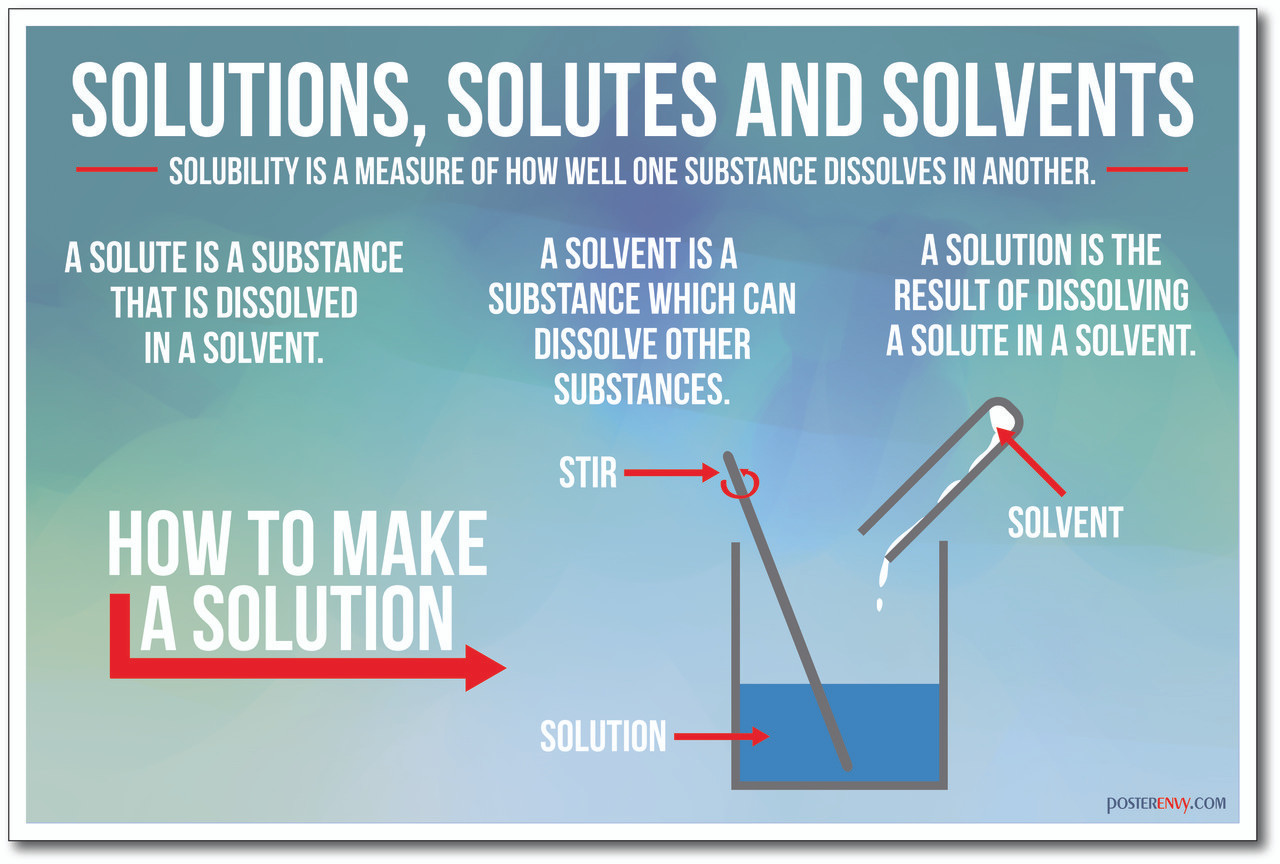
Define Solutes and Solvents: Solutes And Solvents Quick Check

A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances. The substance present in the larger amount is called the solvent, while the substance present in the smaller amount is called the solute.
For example, in a solution of salt water, water is the solvent and salt is the solute. Solvents are usually liquids, but they can also be gases or solids. Solutes can be solids, liquids, or gases.
Types of Solutions
Solutions can be classified into different types based on the concentration of the solute.
- Dilute solutionshave a low concentration of solute.
- Concentrated solutionshave a high concentration of solute.
- Saturated solutionshave the maximum amount of solute that can be dissolved in the solvent at a given temperature.
The concentration of a solution can affect its properties, such as its boiling point, freezing point, and density.
Factors Affecting Solubility, Solutes and solvents quick check
The solubility of a solute in a solvent is influenced by several factors.
- Temperature:The solubility of most solids increases with increasing temperature.
- Pressure:The solubility of gases increases with increasing pressure.
- Solute-solvent interactions:The solubility of a solute in a solvent depends on the interactions between the solute and solvent molecules.
Solution Preparation
Solutions can be prepared by dissolving a known weight of solute in a known volume of solvent.
The concentration of the solution can be calculated using the following formula:
Concentration = (Weight of solute / Volume of solution) x 1000
It is important to use accurate measurements and calculations when preparing solutions.
Applications of Solutions
Solutions have a wide range of applications in various fields.
- Chemistry:Solutions are used in chemical reactions, titrations, and other laboratory procedures.
- Medicine:Solutions are used to deliver drugs, vitamins, and other nutrients to the body.
- Industry:Solutions are used in the production of food, beverages, and other products.
Solutions play an important role in everyday life and industry.
FAQs
What is the difference between a solute and a solvent?
A solute is the substance that dissolves in a solvent, while a solvent is the substance that dissolves the solute.
What are the different types of solutions?
Solutions can be classified based on their solute concentration, such as dilute, concentrated, saturated, and supersaturated solutions.
What factors affect the solubility of a solute?
Temperature, pressure, and solute-solvent interactions all influence the solubility of a solute.
How are solutions prepared?
Solutions can be prepared by dissolving a known mass of solute in a known volume of solvent or by using volumetric glassware to measure the desired concentrations.
What are some applications of solutions?
Solutions have countless applications in chemistry, medicine, industry, and everyday life, such as in cleaning, cooking, and pharmaceuticals.